大厂算法面试之leetcode精讲7.双指针
视频教程(高效学习):点击学习
目录:
1.开篇介绍
2.时间空间复杂度
3.动态规划
4.贪心
5.二分查找
6.深度优先&广度优先
7.双指针
8.滑动窗口
9.位运算
10.递归&分治
11剪枝&回溯
12.堆
13.单调栈
14.排序算法
15.链表
16.set&map
17.栈
18.队列
19.数组
20.字符串
21.树
22.字典树
23.并查集
24.其他类型题
双指针
- 普通指针:两指针同一方向或不同方向
- 对撞指针:两指针互相靠拢
- 快慢指针:一快一慢
141. 环形链表 (easy)
方法1.哈希表或set:
动画过大,点击查看
- 思路:准备一个map或者set,然后循环链表,每次遍历到一个节点的时候,判断当前节点是否在map中存在,如果不存在就把当前节点加入map中,如果存在的话说明之前访问过此节点,也就说明了这条链表有环。
- 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n),n是链表的数量,最差的情况下每个节点都要遍历。空间复杂度O(n),n是存储遍历过的节点的map或者set
js:
var hasCycle = (head) => {
let map = new Map();
while (head) {
if (map.has(head)) return true;//如果当前节点在map中存在就说明有环
map.set(head, true);//否则就加入map
head = head.next;//迭代节点
}
return false;//循环完成发现没有重复节点,说明没环
};
java:
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (!seen.add(head)) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
方法2.快慢指针
动画过大,点击查看
- 思路:准备两个指针fast和slow,循环链表,slow指针初始也指向head,每次循环向前走一步,fast指针初始指向head,每次循环向前两步,如果没有环,则快指针会抵达终点,如果有环,那么快指针会追上慢指针
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
js:
var hasCycle = function (head) {
//设置快慢指针
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
//如果没有环,则快指针会抵达终点,否则继续移动双指针
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
//快慢指针相遇,说明含有环
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
java:
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
142. 环形链表 II (medium)
方法1.哈希表
- 思路:遍历链表,将节点加入一个set中,每次判断当前节点是否在set中,如果存在重复的节点,这个节点就是入环节点
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
js:
var detectCycle = function(head) {
const visited = new Set();
while (head !== null) {//终止条件,如果没有环 跳出循环
if (visited.has(head)) {//如果存在重复的节点,这个节点就是入环节点
return head;
}
visited.add(head);//将节点加入set中
head = head.next;
}
return null;
};
java:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode pos = head;
Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (pos != null) {
if (visited.contains(pos)) {
return pos;
} else {
visited.add(pos);
}
pos = pos.next;
}
return null;
}
}
方法2.快慢指针
动画过大,点击查看
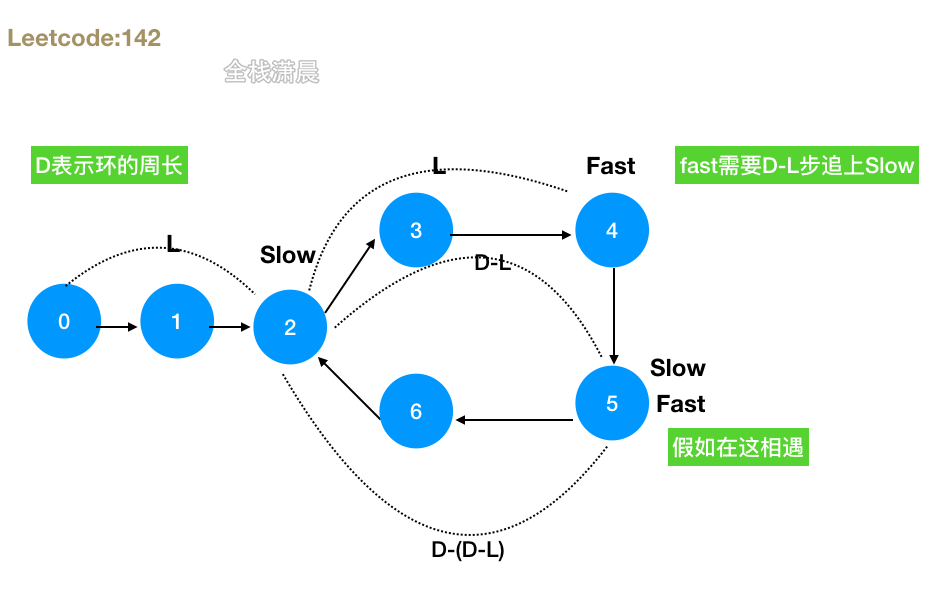
- 思路:慢指针移动两步,快指针移动一步,相遇之后,快指针变成头指针,然后每次快慢指针各走一步直到相遇,相遇的节点就是入环节点
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
js:
var detectCycle = function(head) {
if (head === null) {
return null;
}
let slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast !== null) {
slow = slow.next;//慢指针移动两步,快指针移动一步
if (fast.next !== null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
} else {
return null;//如果没有环 之间返回null
}
if (fast === slow) {//有环
let fast = head;
//快指针指向头节点,然后每次快慢指针各走一步直到相遇,相遇的节点就是入环节点
while (fast !== slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return null;
};
java:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
if (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
} else {
return null;
}
if (fast == slow) {
ListNode fast1 = head;
while (fast1 != slow) {
fast1 = fast1.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast1;
}
}
return null;
}
}
15. 三数之和 (medium)
方法1.暴力求解,对于三个数字,循环3次,分别计算和,时间复杂度O(n^3)
方法2.c=-(a+b): 确定了a和b,那就可以想两数之和一样,在map中寻找-(a+b),减少一层循环,时间复杂度O(n^2),空间复杂度O(n)。
方法3.排序然后查找
动画过大,点击查看
- 思路:先排序数组,数组长度必须大于3,循环数组,假如当前循环到了i索引,则定义两个指针
L = i+1,和R = nums.length-1,如果和sum=nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R]小于0,则向右移动左指针,如果sum大于0,则左移右指针,如果sum等于0,则正好找到了这3个数,然后在尝试L++,R--,继续寻找中间是否有三个数之和等于0,注意在循环的过程中遇见相同的三个数需要去重。 - 复杂度分析:时间复杂度
O(n^2),n为数组的长度。空间复杂度O(logn),即排序所需要的空间
js:
var threeSum = function(nums) {
let ans = [];
const len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len < 3) return ans;//数组的长度大于3
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b); // 排序
for (let i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if(nums[i] > 0) break; // 如果当前数字大于0,则三数之和一定大于0,所以结束循环
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // 去重
let L = i+1;
let R = len-1;
while(L < R){//虽然里面还有两个循环,但是整体的L和R移动的时间内复杂度还是o(n)
const sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if(sum == 0){
ans.push([nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]]);
while (L<R && nums[L] == nums[L+1]) L++; // 去重
while (L<R && nums[R] == nums[R-1]) R--; // 去重
L++;
R--;
}
else if (sum < 0) L++;
else if (sum > 0) R--;
}
}
return ans;
};
java:
class Solution {
public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList();
int len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len < 3) return ans;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if(nums[i] > 0) break; // 如果当前数字大于0,则三数之和一定大于0,所以结束循环
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // 去重
int L = i+1;
int R = len-1;
while(L < R){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if(sum == 0){
ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
while (L<R && nums[L] == nums[L+1]) L++; // 去重
while (L<R && nums[R] == nums[R-1]) R--; // 去重
L++;
R--;
}
else if (sum < 0) L++;
else if (sum > 0) R--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
11. 盛最多水的容器 (medium)
方法1:双指针
动画过大,点击查看
- 思路:用双指针i,j循环height数,i,j对应高度较小的那个先向内移动,不断计算面积,更新最大面积
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),n是数组height的长度,遍历一次。空间复杂度O(1)
js:
var maxArea = function(height) {
let max = 0;
for (let i = 0, j = height.length - 1; i < j;) {//双指针i,j循环height数组
//i,j较小的那个先向内移动 如果高的指针先移动,那肯定不如当前的面积大
const minHeight = height[i] < height[j] ? height[i++] : height[j--];
const area = (j - i + 1) * minHeight;//计算面积
max = Math.max(max, area);//更新最大面积
}
return max;
};
java:
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int i = 0, j = height.length - 1, max = 0;
while(i < j) {
max = height[i] < height[j] ?
Math.max(max, (j - i) * height[i++]):
Math.max(max, (j - i) * height[j--]);
}
return max;
}
}
160. 相交链表 (easy)
方法1:哈希表
- 思路:将链表A存入set中,第一个相同的节点就是重合的节点
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(m+n),m、n分别是两个链表的长度。空间复杂度O(m)
js:
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
const visited = new Set();
let temp = headA;
while (temp !== null) {//将链表A存入set中
visited.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp !== null) {
if (visited.has(temp)) {//第一个相同的节点就是重合的节点
return temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
};
Java:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<ListNode>();
ListNode temp = headA;
while (temp != null) {
visited.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp != null) {
if (visited.contains(temp)) {
return temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}
方法2:双指针
动画过大,点击查看
- 思路:用双指针pA 、pB循环俩个链表,链表A循环结束就循环链表B,链表A循环结束就循环链表B,当
pA == pB时就是交点,因为两个指针移动的步数一样 - 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(m+n),m、n分别是两个链表的长度。空间复杂度O(1)
js:
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
if (headA === null || headB === null) {
return null;
}
let pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA !== pB) {
pA = pA === null ? headB : pA.next;//链表A循环结束就循环链表B
pB = pB === null ? headA : pB.next;//链表A循环结束就循环链表B
}
return pA;//当pA == pB时就是交点
};
java:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
876. 链表的中间结点(easy)
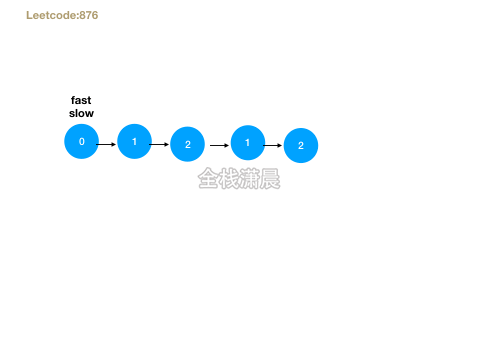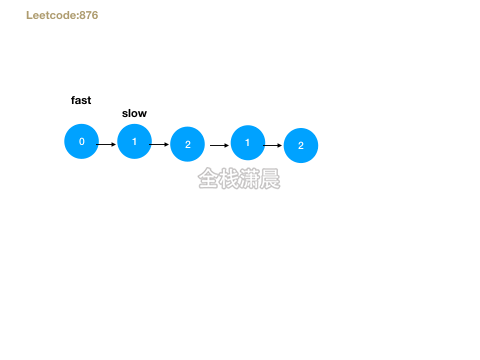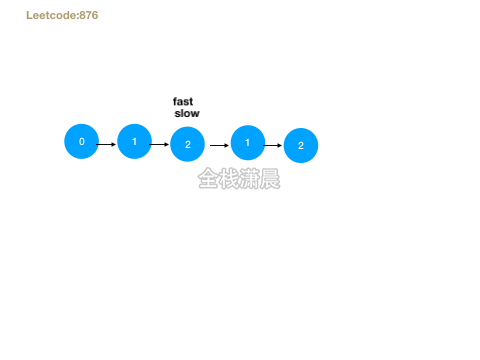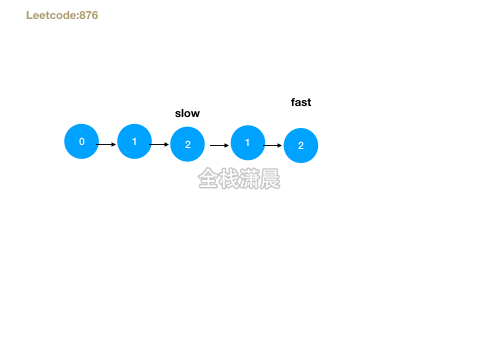
- 思路:快慢指针遍历,直到快指针到达最后
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
js:
var middleNode = function(head) {
slow = fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {//快慢指针遍历,直到快指针到达最后
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
};
java:
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
