第五课 SpringBoot2基础-拦截器、文件上传、异常处理、原生组件和定制组件
tags:
- Spring Boot
- 2021尚硅谷
- 雷丰阳
文章目录
- 第五课 SpringBoot2基础-拦截器、文件上传、异常处理、原生组件和定制组件
- 第一节 拦截器
- 1.1 HandlerInterceptor 接口
- 1.2 拦截器原理
- 第二节 文件上传
- 2.1 文件上传功能实现
- 2.2 文件上传原理
- 第三节 异常处理
- 2.1 默认规则
- 2.2 异常处理自动配置原理
- 2.3 异常处理步骤流程
- 2.4 定制错误处理逻辑
- 第四节 原生组件注入(Servlet、Filter、Listener)
- 4.1 使用Servlet API方式注入
- 4.2 使用RegistrationBean方式注入
- 第五节 嵌入式Servlet容器
- 5.1 切换嵌入式Servlet容器
- 5.2 定制Servlet容器
- 第六节 定制化原理
- 6.1 定制化的常见方式
- 6.2 定制化原理分析套路
第一节 拦截器
1.1 HandlerInterceptor 接口
- 拦截器在底层是
HandlerInterceptor接口有三个方法- preHandle 目标方法处理之前处理
- postHandle 目标方法处理之后没有渲染页面
- afterCompletion 页面渲染之后清理工作
- 使用拦截器做登陆检查
- 创建拦截器类
interceptor.LoginInterceptor去继承HandlerInterceptor - 创建配置类
config.AdminWebConfig重写addInterceptors - 指定拦截规则 ** 如果是拦截所有,静态资源也会被拦截**
- 创建拦截器类
- 创建拦截器类
package com.atguigu.interceptor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
/**
* 拦截器做登陆检查
* 必须实现HandlerInterceptor接口
* 1. 配置好拦截器要拦截哪些请求(AdminWebConfig中配置)
* 2. 把这些配置放在容器中(重写addInterceptors)
* 3. 指定拦截规则【如果是拦截所有,静态资源也会被拦截】
*/
@Slf4j
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 目标方法执行之前
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("拦截的请求路径是{}", requestURI);;
// 登陆检查逻辑
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
Object loginUser = session.getAttribute("loginUser");
if (loginUser != null){
// 放行
return true;
}
// 拦截住 没登录 跳转到登录页
request.setAttribute("msg", "请先登录");
// response.sendRedirect("/"); //这个取不到msg 直接转发
request.getRequestDispatcher("/").forward(request, response);
return false;
}
/**
* 目标方法执行之后
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
log.info("postHandle执行{}",modelAndView);
}
/**
* 页面渲染之后
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
log.info("afterCompletion执行异常{}",ex);
}
}
- 创建配置类
package com.atguigu.config;
import com.atguigu.interceptor.LoginInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class AdminWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**") // 这种情况下所有请求都会被拦截 包括静态资源也会拦截
.excludePathPatterns("/","/login","/css/**","/fonts/**","/images/**","/js/**"); //放行的请求
}
}
- 如果不使用
.excludePathPatterns("/","/login","/css/**","/fonts/**","/images/**","/js/**");放行静态资源。也可以在配置文件中配置。
# 这样静态资源前都要加/static/
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/**
1.2 拦截器原理
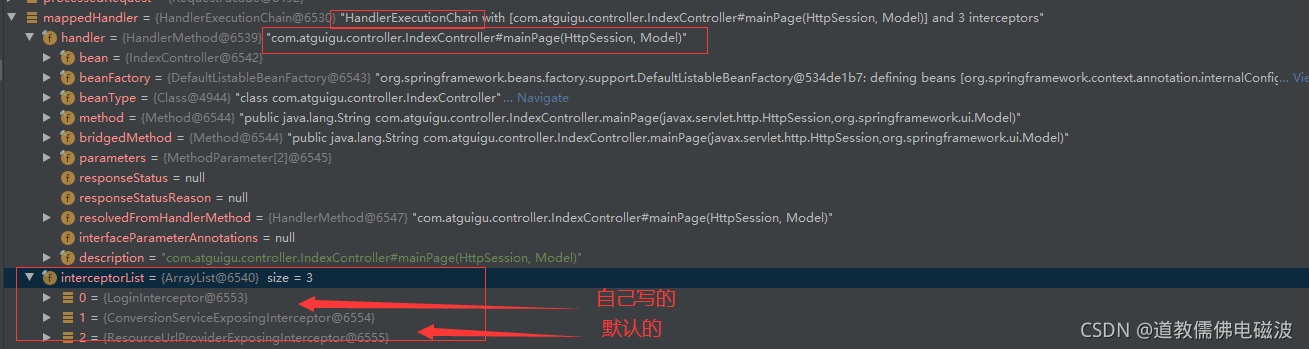
- 断点mainPage中,根据当前请求,找到
HandlerExecutionChain可以处理请求的handler以及handler的所有拦截器。
- 目标方法执行前先执行拦截器的
applyPreHandle。跟踪进去
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
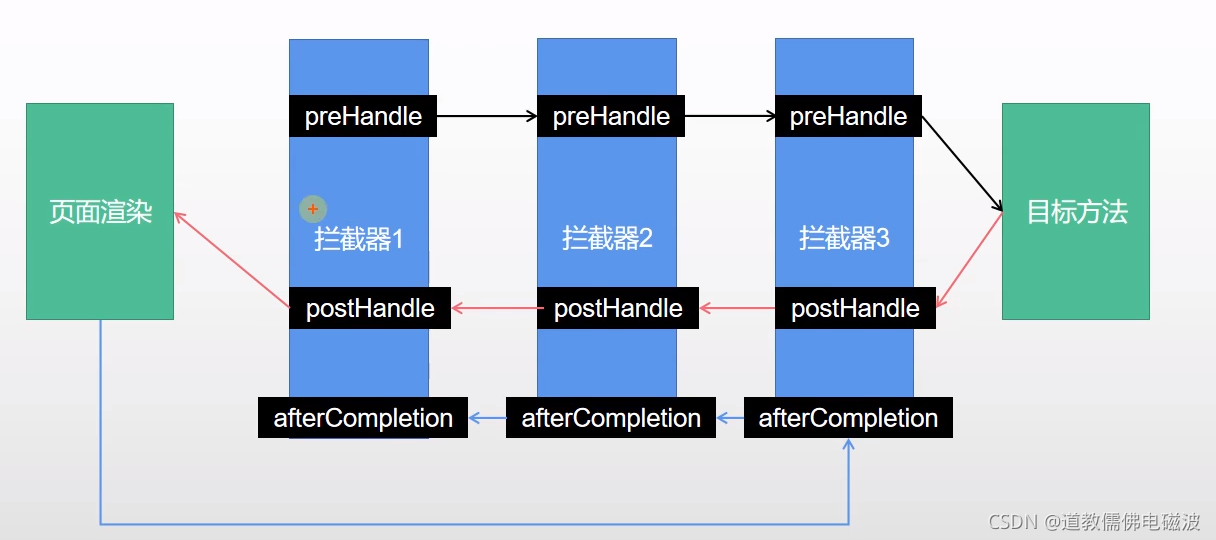
- 挨个遍历拦截器。它去调用了
preHandle方法。先来顺序执行 所有拦截器的 preHandle方法- 如果当前拦截器prehandler返回为true。则执行下一个拦截器的preHandle
- 如果当前拦截器返回为false。直接 倒序执行所有已经执行了的拦截器的
afterCompletion;就是把之前执行过的的清理一下而已
- 如果任何一个拦截器返回false。直接跳出,不执行目标方法
- 所有拦截器都返回True。执行目标方法
6、倒序执行所有拦截器的postHandle方法。
7、前面的步骤有任何异常都会直接倒序触发 afterCompletion
8、页面成功渲染完成以后,也会倒序触发 afterCompletion
第二节 文件上传
2.1 文件上传功能实现
- 写一个
FormTestController控制器
package com.atguigu.controller;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestPart;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 文件上传测试
*/
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class FormTestController {
@GetMapping("/form_layouts")
public String form_layout(){
return "form/form_layouts";
}
/**
* MultipartFile自动封装上传过来的文件
* @param email
* @param username
* @param headerImg
* @param photos
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(@RequestParam("email") String email,
@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestPart("headerImg") MultipartFile headerImg,
@RequestPart("photos") MultipartFile[] photos) throws IOException {
log.info("上传的信息: email={}, username={}, headerImg={},photos={}", email,
username, headerImg.getSize(), photos.length);
if (headerImg.isEmpty()){
// 保存到文件服务器 或oss服务器
String originalFilename = headerImg.getOriginalFilename();
headerImg.transferTo(new File("D:\\" + originalFilename));
}
if (photos.length > 0){
for (MultipartFile photo : photos){
if (!photo.isEmpty()){
String originalFilename = photo.getOriginalFilename();
photo.transferTo(new File("D:\\" + originalFilename));
}
}
}
return "main";
}
}
- 配置文件设置上传文件的大小
# 每个上传文件的大小设置
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB
# 一个请求中所有文件上传大小设置
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=100MB
2.2 文件上传原理
- ctrl + N 搜索
MultipartAutoConfiguration- 自动配置好了StandardServletMultipartResolver 文件上传参数解析器(只能解析Servlet方式上传的文件)
- 原理步骤
- 还是从DispatcherServlet#doDispatch 追踪
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);如果是Multipart,把请求重新包装一下。 - 参数解析器来解析请求中的文件内容封装成MultipartFile
- 将request中文件信息封装为一个Map;MultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile>
FileCopyUtils。实现文件流的拷贝
- 还是从DispatcherServlet#doDispatch 追踪
第三节 异常处理
2.1 默认规则
- 官方网站:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/features.html#features.developing-web-applications.spring-mvc.error-handling
- 默认情况下,Spring Boot提供/error处理所有错误的映射
- 对于机器客户端,它将生成JSON响应,其中包含错误,HTTP状态和异常消息的详细信息。
- 对于浏览器客户端,响应一个“ whitelabel”错误视图,以HTML格式呈现相同的数据
- 自定义错误页-放到templates的error中
- error/404.html error/5xx.html;有精确的错误状态码页面就匹配精确,没有就找 4xx.html;如果都没有就触发白页
2.2 异常处理自动配置原理
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration自动配置异常处理规则- 容器中的组件一:类型:
DefaultErrorAttributes-> id:errorAttributes (默认方法名作为id) 跟踪进去public class DefaultErrorAttributes implements ErrorAttributes, HandlerExceptionResolver- DefaultErrorAttributes:定义错误页面中可以包含哪些数据属性。需要定制页面的中的属性需要定义它。
- 容器中的组件二:类型:
BasicErrorController--> id:basicErrorController(响应json或者白页 适配响应) 点进去看到。需要定制跳转逻辑需要定义它。- 处理默认 /error 路径的请求;页面响应 new ModelAndView(“error”, model);
- 容器中有组件 View->id是error;(响应默认错误页)
WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration - 容器中放组件 BeanNameViewResolver(视图解析器);按照返回的视图名error作为组件的id去容器中找View对象。
- 如果想要返回页面;就会找error视图【StaticView】。(默认是一个白页)
- 容器中的组件三:类型:
DefaultErrorViewResolver-> id:conventionErrorViewResolver 点进去看到。需要定义错误页面的路径需要定义它。- 如果发生错误,会以HTTP的状态码 作为视图页地址(viewName),找到真正的页面
- error/404、5xx.html
2.3 异常处理步骤流程
- 执行目标方法
ha.handle,目标方法运行期间有任何异常都会被catch、而且标志当前请求结束;并且用 dispatchException - 进入视图解析流程(页面渲染?)
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); mv = processHandlerException处理handler发生的异常,处理完成返回ModelAndView;- 遍历所有的 handlerExceptionResolvers,看谁能处理当前异常【HandlerExceptionResolver处理器异常解析器】
- DefaultErrorAttributes系统默认的 异常解析器;
- 追踪进去
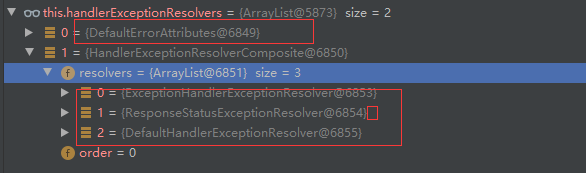
- DefaultErrorAttributes先来处理异常。把异常信息保存到rrequest域,并且返回null;默认没有任何人能处理异常,所以异常会被抛出
- 1、如果没有任何人能处理最终底层就会发送/error请求。会被底层的
BasicErrorController处理. - 2、解析错误视图;遍历所有的
ErrorViewResolver看谁能解析。 - 3、默认的DefaultErrorViewResolver ,作用是把响应状态码作为错误页的地址,error/500.html
- 4、模板引擎最终响应这个页面error/500.html
- 1、如果没有任何人能处理最终底层就会发送/error请求。会被底层的
2.4 定制错误处理逻辑
- 第一种:自定义错误页
- error/404.html error/5xx.html;有精确的错误状态码页面就匹配精确,没有就找 4xx.html;如果都没有就触发白页
- 400错误码:不带请求参数或者参数类型不对;Bad Request一般都是浏览器的参数没有传递正确
- 第二种(推荐使用):@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler处理全局异常;底层是异常处理器第二个中的第一个ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 支持的
package com.atguigu.exception;
/*
* 处理整个web的controller异常
*/
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class, NullPointerException.class}) // 异常处理器 处理异常
public String handleArithException(Exception e){
log.error("异常是: {}", e);
return "login"; // 视图地址
}
}
- 第三种:**@ResponseStatus+自定义异常 **;底层是第二个中的第二个
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver, 把responsestatus注解的信息底层调用response.sendError(statusCode, resolvedReason);最终tomcat发送的/error,而这个请求同时也结束了。
@GetMapping("/dynamic_table")
public String dynamic_table(Model model){
//表格内容的遍历
//response.sendError
List<User> users = Arrays.asList(new User("zhangsan", "123456"),
new User("lisi", "123444"),
new User("haha", "aaaaa"),
new User("hehe ", "aaddd"));
model.addAttribute("users",users);
if(users.size()>3){
throw new UserTooManyException();
}
return "table/dynamic_table";
}
package com.atguigu.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value= HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN,reason = "用户数量太多")
public class UserTooManyException extends RuntimeException {
public UserTooManyException(){
}
public UserTooManyException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
- 第四种:Spring底层的异常,如 参数类型转换异常;第二个的第三个
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver处理框架底层的异常。response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, ex.getMessage());
@GetMapping("/basic_table")
public String basic_table(@RequestParam("a") int a){
int i = 10/0;
return "table/basic_table";
}
- 第五种: 自定义实现 HandlerExceptionResolver 处理异常 ;可以作为默认的全局异常处理规则。需要定义优先级,防止被默认异常处理器提前处理了。
package com.atguigu.exception;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@Order(value= Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) //优先级,数字越小优先级越高
@Component
public class CustomerHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
response.sendError(511,"我喜欢的错误");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new ModelAndView();
}
}
- ErrorViewResolver 实现自定义处理异常;
- response.sendError 。error请求就会转给controller
- 你的异常没有任何人能处理。tomcat底层 response.sendError。error请求就会转给controller
- basicErrorController 要去的页面地址是 ErrorViewResolver 解析的 ;保底的异常处理,所有没被处理的异常都会被它捕获。
第四节 原生组件注入(Servlet、Filter、Listener)
4.1 使用Servlet API方式注入
- 第一步:
@ServletComponentScan(basePackages = "com.atguigu.admin")在启动类中添加 :指定原生Servlet组件都放在那里。推荐可以这种方式;
// com.atguigu.Boot05WebAdminApplication 启动类
package com.atguigu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
@ServletComponentScan(basePackages = "com.atguigu")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Boot05WebAdminApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Boot05WebAdminApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 第二步:实现下面的一种原生组件的注入。
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/my"):效果:直接响应,没有经过Spring的拦截器.@WebFilter(urlPatterns={"/css/*","/images/*"})@WebListener
// WebServlet
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/my")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("666666");
}
}
// @WebFilter
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = {"/css/*", "/images/*"})
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
log.info("MyFilter初始化完成;");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("MyFilter工作");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("MyFilter销毁;");
}
}
// WebListener
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
@Slf4j
@WebListener
public class MySwervletContextListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
log.info("MySwervletContextListener监听到项目初始化完成");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
log.info("MySwervletContextListener监听到项目销毁");
}
}
- 扩展:DispatchServlet 如何注册进来
- 容器中自动配置了 DispatcherServlet 属性绑定到 WebMvcProperties;对应的配置文件配置项是 spring.mvc。
- 通过
ServletRegistrationBean<DispatcherServlet> 把 DispatcherServlet配置进来。 - 默认映射的是 / 路径。
# 可以修改servlet的默认路径
spring.mvc.servlet.path=/mvc/
- Tomcat-Servlet;多个Servlet都能处理到同一层路径,精确优选原则
- A: /my/
- B: /my/1
4.2 使用RegistrationBean方式注入
ServletRegistrationBean,FilterRegistrationBean, andServletListenerRegistrationBean
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletListenerRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 1、MyServlet --> /my
* 2、DispatcherServlet --> /
*/
// (proxyBeanMethods = true):保证依赖的组件始终是单实例的
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true)
public class MyRegistConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet(){
MyServlet myServlet = new MyServlet();
return new ServletRegistrationBean(myServlet,"/my","/my02");
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter(){
MyFilter myFilter = new MyFilter();
// return new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter,myServlet());
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter);
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/my","/css/*"));
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener(){
MySwervletContextListener mySwervletContextListener = new MySwervletContextListener();
return new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(mySwervletContextListener);
}
}
第五节 嵌入式Servlet容器
5.1 切换嵌入式Servlet容器
- 默认支持的webServer(官网手册7.4.3)
- Tomcat, Jetty, or Undertow
ServletWebServerApplicationContext容器启动寻找ServletWebServerFactory 并引导创建服务器
- 切换服务器(如果不想用默认Tomcat服务器, 修改下面配置 排除exclusion,加入其它服务器配置)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
- 原理
- SpringBoot应用启动发现当前是Web应用。web场景包-导入tomcat
- web应用会创建一个web版的ioc容器
ServletWebServerApplicationContext - ServletWebServerApplicationContext 启动的时候寻找
ServletWebServerFactory(Servlet 的web服务器工厂—> Servlet 的web服务器) - SpringBoot底层默认有很多的WebServer工厂;
TomcatServletWebServerFactory,JettyServletWebServerFactory, orUndertowServletWebServerFactory - 底层直接会有一个自动配置类。
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration导入了ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration(配置类) ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration配置类 根据动态判断系统中到底导入了那个Web服务器的包。(默认是web-starter导入tomcat包),容器中就有TomcatServletWebServerFactoryTomcatServletWebServerFactory创建出Tomcat服务器并启动;TomcatWebServer 的构造器拥有初始化方法initialize—this.tomcat.start();- 内嵌服务器,就是手动把启动服务器的代码调用(tomcat核心jar包存在)
5.2 定制Servlet容器
- 实现
WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>- 把配置文件的值和ServletWebServerFactory 进行绑定
- 第一种:修改配置文件 server.xxx 比如:
server.tomcat.accesslog.max-days=10
- 第二种:直接自定义 ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory
- 第三种:xxxxxCustomizer:定制化器,可以改变xxxx的默认规则
第六节 定制化原理
6.1 定制化的常见方式
- 修改配置文件;
- xxxxxCustomizer;**定制化器 **
- 编写自定义的配置类 xxxConfiguration;+ @Bean替换、增加容器中默认组件;视图解析器
- Web应用 编写一个配置类实现 WebMvcConfigurer 即可定制化web功能;+ @Bean给容器中再扩展一些组件
@Configuration
public class AdminWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer
- @EnableWebMvc + WebMvcConfigurer —— @Bean 可以全面接管SpringMVC,所有规则全部自己重新配置, 比如静态资源,视图解析器,默认页面等需要自己配置; 实现定制和扩展功能
- 原理
WebMvcAutoConfiguration默认的SpringMVC的自动配置功能类。静态资源、欢迎页等等- 一旦使用 @EnableWebMvc 、。会 @Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
- DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 的 作用,只保证SpringMVC最基本的使用
- 把所有系统中的 WebMvcConfigurer 拿过来。所有功能的定制都是这些 WebMvcConfigurer 合起来一起生效
- 自动配置了一些非常底层的组件。RequestMappingHandlerMapping、这些组件依赖的组件都是从容器中获取
- public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport
- WebMvcAutoConfiguration 里面的配置要能生效 必须
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class) - @EnableWebMvc 导致了 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 没有生效。基本的已经有了默认的配置就不生效了。
6.2 定制化原理分析套路
- 场景starter - xxxxAutoConfiguration - 导入xxx组件 - 绑定xxxProperties – 绑定配置文件项
