决胜机房奥林匹克之LCA篇
前置知识:
二叉树
LCA:
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3379
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
LCA(Least Common Ancestors),即最近公共祖先,是指在有根树
中,找出某两个结点u和v最近的公共祖先。 ———来自百度百科
比方说样例:
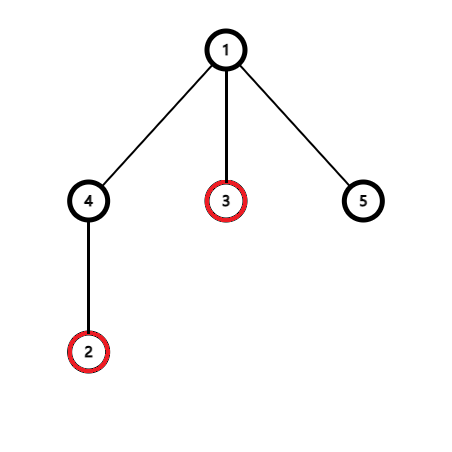
要你求3号点和2号点的lca。
显然,答案唯一,为根节点。
所以,lca有为一解,且必定有解。
那么,我们改如何去求解LCA呢?
暴力算法
考虑记录一下当前节点的深度。先让较深的那个节点跳到和另一个节点相同的深度(高度),再让两个节点一步一步地跳上去,直到跳到同意高度。
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 500005;
#define int long long
vector <int> p[maxn];
int f[maxn], dep[maxn];//dep记录深度,f[i]记录第i个点的父亲
void dfs(int x, int father){
// cout<<x<<' ';
f[x] = father;
dep[x] = dep[f[x]] + 1;
int l = p[x].size();
for(int i = 0; i < l; i++){
if(p[x][i] != father) dfs(p[x][i], x);//这里是为了防止重复遍历一个点
}
return ;
}
int lca(int x, int y){
if(dep[x] < dep[y]) swap(x, y);//如果x的深度浅与y,则交换两数
while(dep[x] > dep[y]){
x = f[x];//让较深的那个节点跳到和另一个节点相同的深度(高度)
}
if(x == y){
return x;//注意这里如果已经求出答案了就直接return
}
while(x != y){
x = f[x], y = f[y];//两个点一起爬
}
return x;
}
signed main(){
int n, m, s;
cin>>n>>m>>s;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int x, y;
cin>>x>>y;
p[x].push_back(y);
p[y].push_back(x);
}
dfs(s, s); //注意根节点的父亲是它本身
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int x, y;
cin>>x>>y;
cout<<lca(x, y)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
这玩意预处理 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),每次查询 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),所以复杂度应该是 O ( n m ) O(nm) O(nm)吧?
倍增优化
先鸽着
